Why Do I Need Dark Web Monitoring?
Dark Web monitoring fills an important security gap for individuals and businesses. It has applications in cyber security, reputation management and brand management. By monitoring Dark Web activity, individuals and organizations may be alerted to cyber attacks or data breaches.
 Admit it: You search your name on Google to see what’s there. Most businesses pay attention to their online reviews. Some monitor social media to see what customers are saying. Dark Web monitoring completes the picture of your and your organization’s online reputation. It can also tip you off to data breaches or potential cyber attacks.
Admit it: You search your name on Google to see what’s there. Most businesses pay attention to their online reviews. Some monitor social media to see what customers are saying. Dark Web monitoring completes the picture of your and your organization’s online reputation. It can also tip you off to data breaches or potential cyber attacks.
What Is the Dark Web?
In its broadest definition, the Dark Web is a portion of the Deep Web, which itself is a collection of websites and databases that are not indexed by the major search engines (Google, Microsoft Edge, Yahoo!, DuckDuckGo, etc.). In 2018, CNBC estimated that the Deep Web was 400 to 500 times the size of the Internet that most people use.
The Deep Web itself is benign. It consists of password-protected content, encrypted databases and data, including millions of articles, books, recipes and public records. Some of these can be accessed through specialized search engines, such as a university’s library catalog of digital media or LexisNexis.
Amid those terabytes of data lurks a smaller set of sites that can be accessed with browsers such as TOR, short for The Onion Router, a browser that attempts to conceal the user’s location by routing web traffic randomly across the globe. Promises of anonymity and cover from law enforcement have made the Dark Web a haven for illegal activity. It is where many cyber crimes originate, and where you will find cyber criminals offering their services and software for sale alongside the fruits of their labors: credit cards, login credentials and personal information.
Why Are Businesses Monitoring the Dark Web?
Because a great deal of cyber crime originates on the Dark Web, monitoring is a tool that thwarts and reveals attacks. In some cases, it can be the first warning of a data breach.
Dark Web monitoring begins with a deep dive on selected data points. For businesses, this is most commonly the business name and the names of senior executives and managers. This creates a baseline of information that is known to be compromised, as well as intelligence on any discussions about the business or its leaders among cyber criminals. This information is provided to the business with notes on any areas of concern.
Once the baseline is established, the Dark Web is searched on a regular basis for new information. This may include
- Mentions of the business or its leaders by cyber criminals, which can signal a pending attack
- Solicitations to buy or sell information on the business or its leaders
- Newly posted data, which may include compromised logins for systems, user accounts or personal accounts of the company’s leaders
- Customer data, such as credit card numbers, exfiltrated from a company’s database
When new information is found, the business receives an immediate alert that can be used to prepare for or stop a cyber attack. In some cases, this is the first evidence of a data breach that compromises customer information.
Dark Web monitoring may also reveal what people are saying about a business and its employees, providing opportunities to repair reputational damage. It can also be used to prevent disgruntled former employees from selling stolen data online after their separation from a company.
How Can I Monitor the Dark Web?
Dark Web monitoring requires specialized software that can access and index the hundreds of thousands of hidden sites that criminals use to communicate. There is currently no free solution, and until recently, monitoring was an expensive service available only to large companies.
Protect Now is pleased to offer affordable small-business Dark Web monitoring that includes a full baseline examination of data about your business and employees, as well as regular updates on any new information that appears online. If someone adds to that information, attempts to buy or sell it or discusses using it, you will be notified immediately so that you can take action.

 Most of the suggestions and tips that are found in the guide aren’t things that are foreign to people who use Apple products, but there is a
Most of the suggestions and tips that are found in the guide aren’t things that are foreign to people who use Apple products, but there is a 
 If you are planning an upcoming vacation or a business trip, you might be thinking about renting a car. “Smart Cars” are all the rage, and they connect to the internet. You get Bluetooth, navigation, hands-free calling, live-streaming, and much more. In fact, if you have a fairly new car, yourself, you probably already have some access to these features. You probably connect your devices to your car, too, so that you can stream music, text, make phone calls, etc. This is no issue because it’s your own car, and only you and your family are using it.
If you are planning an upcoming vacation or a business trip, you might be thinking about renting a car. “Smart Cars” are all the rage, and they connect to the internet. You get Bluetooth, navigation, hands-free calling, live-streaming, and much more. In fact, if you have a fairly new car, yourself, you probably already have some access to these features. You probably connect your devices to your car, too, so that you can stream music, text, make phone calls, etc. This is no issue because it’s your own car, and only you and your family are using it. It’s possible that your router or any router you connect to has been hacked and you won’t know it. A known tactic called
It’s possible that your router or any router you connect to has been hacked and you won’t know it. A known tactic called  Now while Google upsets many people for many reasons, they do a pretty good job at keeping your email account secure. And they provide a number of tools to accomplish that task. The problem is not usually Google, the problem is usually in the “seat” and that’s you buddy. All of you fools using the same password across multiple accounts are potential victims of “credential stuffing” and those of you using the same pass code across multiple accounts are just, well dumb. No offense. But really, it’s just stupid.
Now while Google upsets many people for many reasons, they do a pretty good job at keeping your email account secure. And they provide a number of tools to accomplish that task. The problem is not usually Google, the problem is usually in the “seat” and that’s you buddy. All of you fools using the same password across multiple accounts are potential victims of “credential stuffing” and those of you using the same pass code across multiple accounts are just, well dumb. No offense. But really, it’s just stupid. One such site is
One such site is 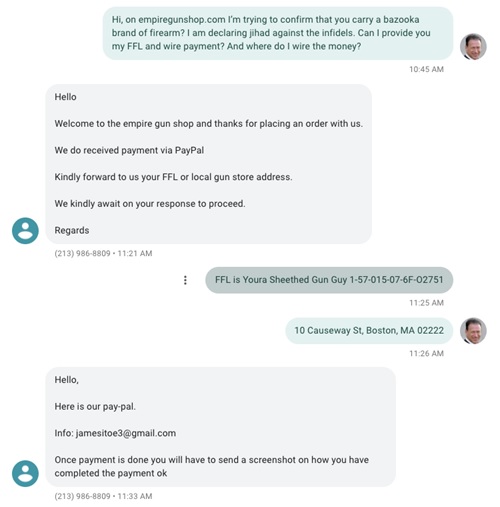
 Stop Your Laptop from Spying
Stop Your Laptop from Spying You might want to put up a photo of your kids and dog opening their gifts on Christmas morning or you and your spouse toasting the New Year, but creeps can easily access the exact location each of these photos were taken, and it’s easier to do than you might think.
You might want to put up a photo of your kids and dog opening their gifts on Christmas morning or you and your spouse toasting the New Year, but creeps can easily access the exact location each of these photos were taken, and it’s easier to do than you might think. Hackers have a saying – “Own the email, and you’ll own the person.” If you get hacked, the scammers will now have access to many, if not all, of the accounts that are associated with your email address.
Hackers have a saying – “Own the email, and you’ll own the person.” If you get hacked, the scammers will now have access to many, if not all, of the accounts that are associated with your email address.























